Structure And Properties Of Ceramic Materials

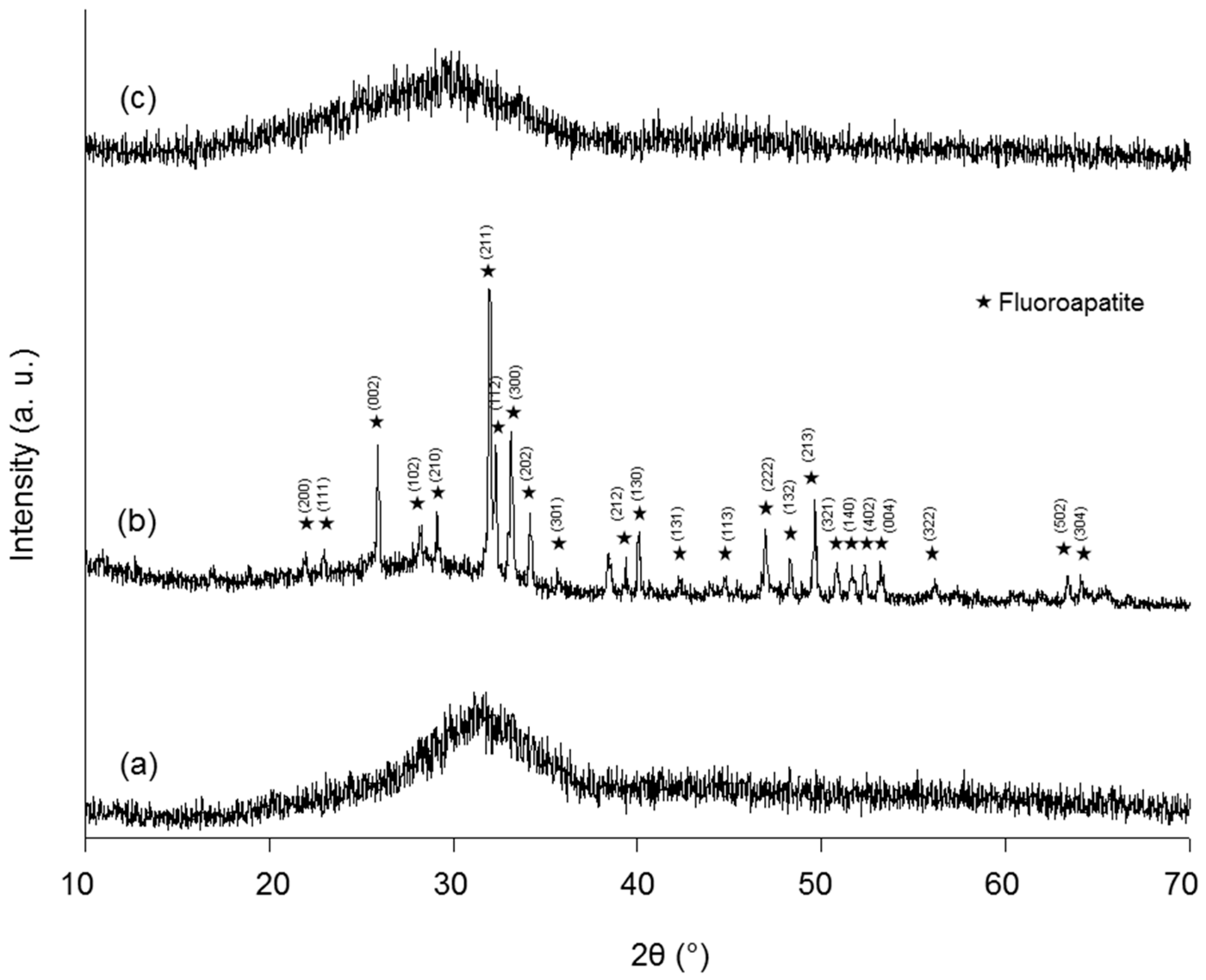
In figures 2a through 2d representative crystal structures are shown that illustrate many of the unique features of ceramic materials.
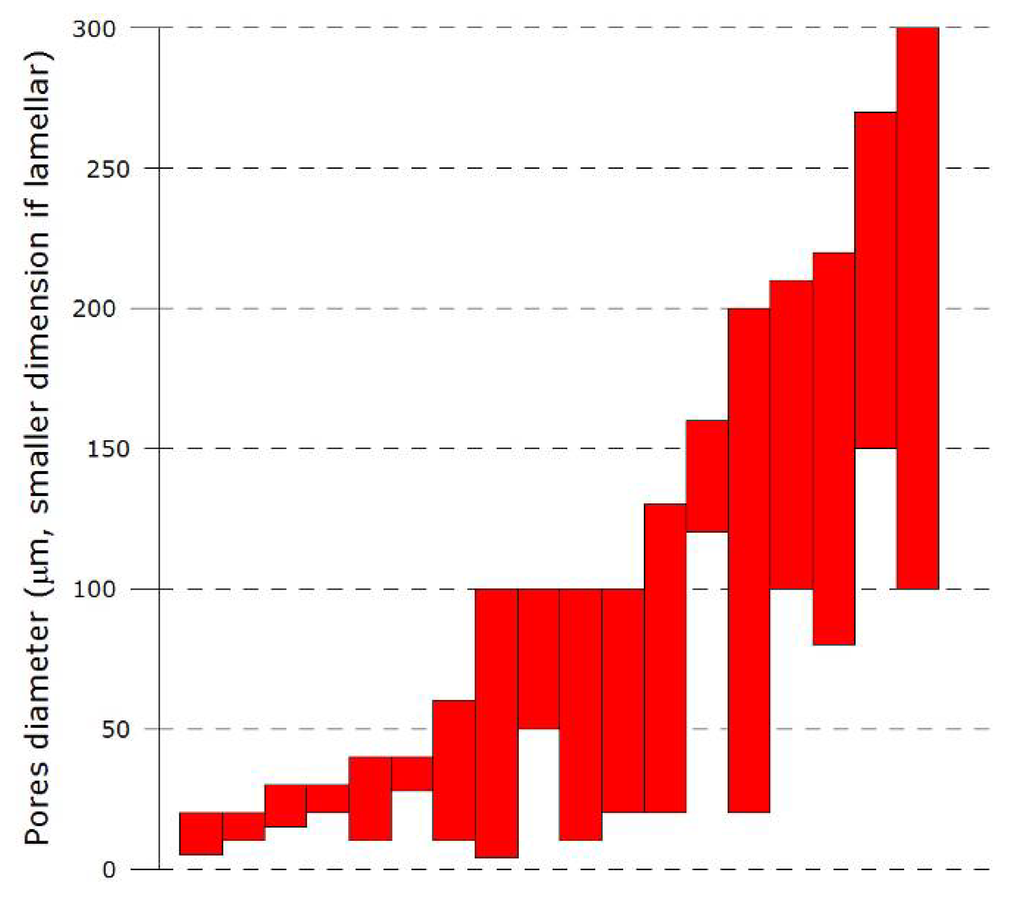
Structure and properties of ceramic materials. Thus in order to fully understand the properties of ceramics a knowledge of their structure is essential. Ceramic materials i 5 structure percentage of ionic and covalent character of the bond for some ceramic materials determines the crystalline structure ceramic material atoms in bond x a x b ionic character covalent character mgo mg o 2 3 73 27 al 2o 3 al o 2 0 63 37 sio 2 si o 1 7 51 49 si 3n 4 si n 1 2 30 70. Generally ceramic particles are fine and coarse. Fundamental information on the bulk properties of biomaterials basic level to enable understanding of metallic polymeric and ceramic substrates in the next few classes we will cover.
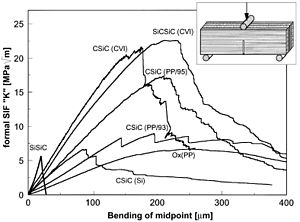
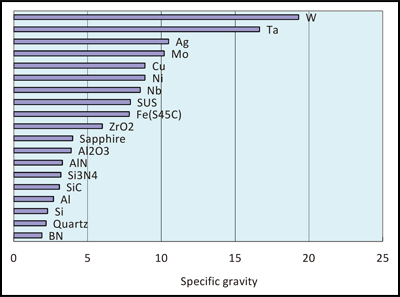
These are very important parameters for the ceramic material. It exhibits the highest mechanical strength and toughness at room temperature. They withstand chemical erosion that occurs in other materials subjected to acidic or caustic environments. Typical zirconia zro 2 properties.
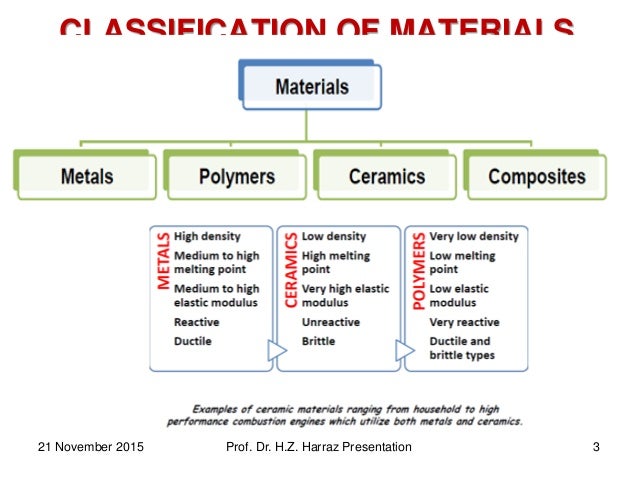
Some elements such as carbon or silicon may be considered ceramics ceramic materials are brittle hard strong in compression and weak in shearing and tension. A common definition of a ceramic is a hard material that is held together with ionic and covalent bonds. The density of ceramics is intermediate between polymers and metals. Dental ceramics are usually composed of nonmetallic inorgani c structures primari ly co ntaining compo unds o f oxy gen w ith o ne or mo re me t all ic o r semi met allic ele ment s.
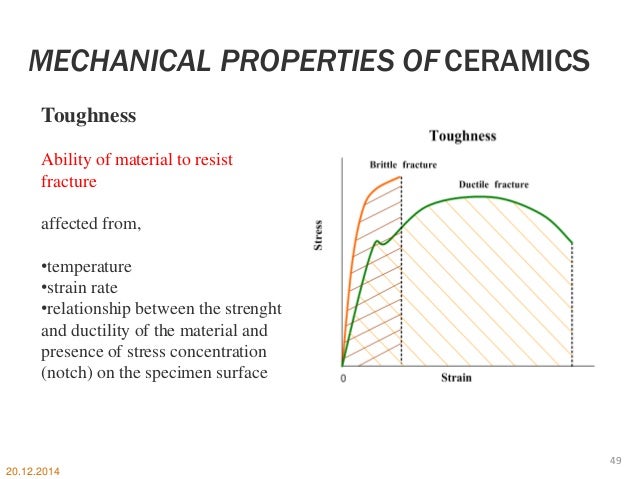
Crystal structure stress strain behavior creep fracture fatigue and wear of materials. Electronic structure and atomic bonding determine microstructure and properties of ceramic and glass materials. We determine the above all properties with the particle sizes of the material. Graphene is currently considered the strongest known material.
A ceramic material is an inorganic non metallic often crystalline oxide nitride or carbide material. It is the primary bonds in ceramics that make them among the strongest hardest and most refractory materials known. Additionally carbon based materials such as carbon fiber carbon nanotubes and graphene can be considered ceramics. Zirconia ceramics have a martensite type transformation mechanism of stress induction which provides the ability to absorb great amounts of stress relative to other ceramic materials.
Introduction to material properties new focus on. Crystalline materials have high density than non crystalline materials. Crystal structure is also responsible for many of the properties of ceramics. According to this definition elemental carbon is a ceramic.
All ceramic materials are prepared by ceramic technology and powder substances are used as the initial raw materials.






















.jpg)